this page shows how to run a spring boot application on local K8S environment.
Objectives
1.create spring boot application and build a docker image
2.create local persistent volume to share the files from host
3.create deployment and service to run this application and expose for external access.
Before you begin
install docker desktop in local and enable local k8s cluster, more details please refer to docker official guide or k8s local cluster setup guide.
Create spring boot application and build docker image
in this demo, created a simple config service using spring boot cloud config, source code on git
Spring boot application - config-service
1.use Spring Cloud Config to quickly implement a config service, please refer to spring cloud documents.
2.create a service config repos on git, in this demo, we will use the native config rather than points to git directly as
network delay caused by GFW.
- service configs - spring:
server:
port: 8888
spring:
application:
name: config-service
profiles:
active: native
cloud:
config:
server:
native:
search-locations: ${CONFIG_ROOT_PATH:${config.root-path}}/config/{application}
bootstrap: true
# git:
# uri: ${CONFIG_REPOSITORY_URL:https://github.com/cloud-poc/service-config.git}
# clone-on-start: true
# #cannot work when use place-holder(not just '{application}')
# search-paths: 'config/{application}'
config.root-path: /Users/jamie/Documents/work-benches/workspace-20190524/service-config
- config repo:
3.test if works
to test if you can get the configs configured in above steps.
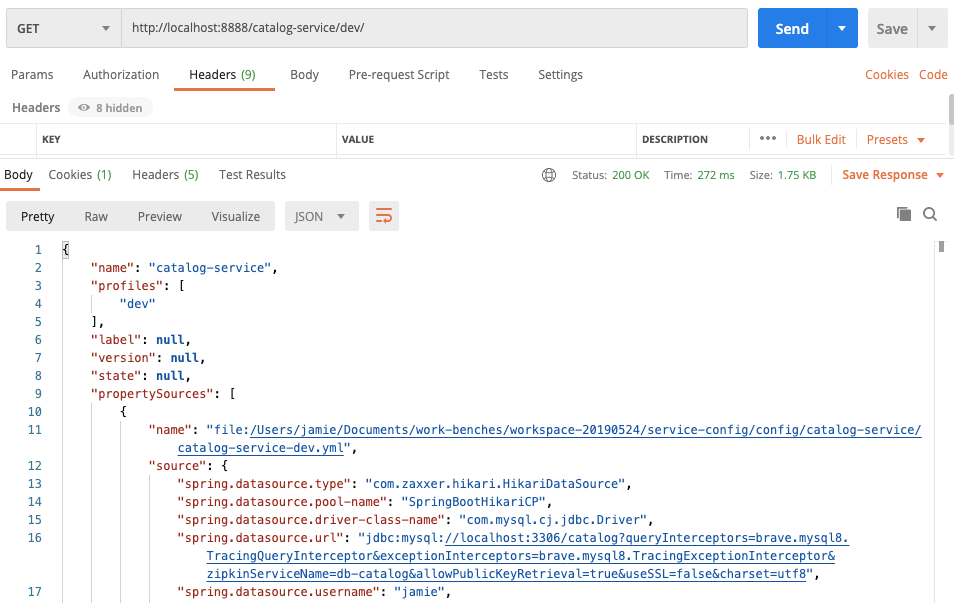 from above screenshot, the configs correctly responded from config server, then let’s move to docker image build.
from above screenshot, the configs correctly responded from config server, then let’s move to docker image build.
Docker image build & push
There are several most widely used Maven plugins for Docker in the open source community, for example, fabric8’s docker-maven-plugin, Spotify’s docker-maven-plugin, Spotify’s dockerfile-maven, and Google’s jib-maven-plugin,etc. We’ll use the jib-maven-plugin for our application, let’s start with its configuration.
- jib-maven-plugin in pom.xml
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>com.google.cloud.tools</groupId>
<artifactId>jib-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>${jib.version}</version>
<configuration>
<from>
<image>openjdk:alpine</image>
</from>
<to>
<image>docker.io/akjamie/${artifactId}:${project.version}</image>
<!-- <credHelper>wincred</credHelper> -->
<credHelper>desktop</credHelper>
</to>
<container>
<creationTime>USE_CURRENT_TIMESTAMP</creationTime>
</container>
<allowInsecureRegistries>true</allowInsecureRegistries>
</configuration>
</plugin>
- command run to build image and push
mvn clean compile jib:build
after finishes, check the result in local and docker hub:

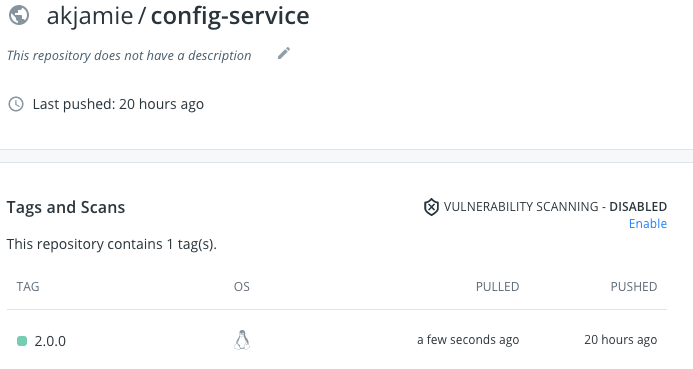
Use Local Persistent Volume to share the service configs
In our application, we’re using the native mode for config server to load the application configs, hence we need to share the files to the pod or container in Kubernates cluster. to achive this goal, what we need to do as following:
- create storage class - sc
- create persistent volume - pv
- create persistent volume claim - pvc
Create storage class
config file - k8s-localpv-storage-class.yml
kind: StorageClass
apiVersion: storage.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: local-storage
provisioner: kubernetes.io/no-provisioner
volumeBindingMode: WaitForFirstConsumer
detailed configs please refer to https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/storage/storage-classes/
use command to create storage class
kubectl apply -f k8s-localpv-storage-class.yml
Create persistent volume
config file - k8s-localpv-persistent-volume.yml
apiVersion: v1
kind: PersistentVolume
metadata:
name: local-pv-service-config
spec:
capacity:
storage: 100Mi
accessModes:
- ReadOnlyMany
persistentVolumeReclaimPolicy: Retain
storageClassName: local-storage
local:
path: /Users/jamie/Documents/work-benches/k8s-sandbox
nodeAffinity:
required:
nodeSelectorTerms:
- matchExpressions:
- key: kubernetes.io/hostname
operator: In
values:
- docker-desktop
1.spec.local.path, specify the path in host you want to share with k8s cluster
2.spec.accessModes, here we want to share the service configs for centralized configuration management, only allow pod/container to consume it rather than modify.
similar command should use here to create PV.
kubectl apply -f k8s-localpv-persistent-volume.yml
https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/storage/persistent-volumes/
Create PVC
config file - k8s-localpv-pv-claim.yml
kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
name: pvc-config-service
spec:
accessModes:
- ReadOnlyMany
storageClassName: local-storage
resources:
requests:
storage: 100Mi
Verify the resource created
use kubectl command to check the resource we created in above 3 steps.
Jamies-MacBook-Pro:scripts jamie$ kubectl get sc
NAME PROVISIONER AGE
hostpath (default) docker.io/hostpath 174d
local-storage kubernetes.io/no-provisioner 21h
Jamies-MacBook-Pro:scripts jamie$ kubectl get pv
NAME CAPACITY ACCESS MODES RECLAIM POLICY STATUS CLAIM STORAGECLASS REASON AGE
local-pv-service-config 100Mi ROX Retain Bound default/pvc-config-service local-storage 10h
pvc-8fa57c9e-b10d-4ee4-ae9a-f794189e16e2 100Mi RWO Delete Bound default/example-local-claim hostpath 172d
Jamies-MacBook-Pro:scripts jamie$ kubectl get pvc
NAME STATUS VOLUME CAPACITY ACCESS MODES STORAGECLASS AGE
example-local-claim Bound pvc-8fa57c9e-b10d-4ee4-ae9a-f794189e16e2 100Mi RWO hostpath 172d
pvc-config-service Bound local-pv-service-config 100Mi ROX local-storage 10h
Jamies-MacBook-Pro:scripts jamie$ kubectl describe sc/local-storage
Name: local-storage
IsDefaultClass: No
Annotations: kubectl.kubernetes.io/last-applied-configuration={"apiVersion":"storage.k8s.io/v1","kind":"StorageClass","metadata":{"annotations":{},"name":"local-storage"},"provisioner":"kubernetes.io/no-provisioner","volumeBindingMode":"WaitForFirstConsumer"}
Provisioner: kubernetes.io/no-provisioner
Parameters: <none>
AllowVolumeExpansion: <unset>
MountOptions: <none>
ReclaimPolicy: Delete
VolumeBindingMode: WaitForFirstConsumer
Events: <none>
Deploy application and share the access entry
Application deployment
config for deployment in K8S
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: config-service-deployment
labels:
app: config-service
spec:
replicas: 2
selector:
matchLabels:
app: config-service
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: config-service
spec:
containers:
- name: config-service
image: docker.io/akjamie/config-service:2.0.0
env:
- name: CONFIG_ROOT_PATH
value: "/app/data/service-configs"
ports:
- containerPort: 8888
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: "/app/data"
name: storage
volumes:
- name: storage
persistentVolumeClaim:
claimName: pvc-config-service
1.spec.replicas, as name depicts, how many replicas of the application you want to run 2.spec.containers.volumeMounts.mountPath, we mount the service configs path defined in local persistent volume to ‘/app/data/service-configs’, so that use it to set the env variable CONFIG_ROOT_PATH, CONFIG_ROOT_PATH will override the ‘search-locations’ defined in bootstrap.yml
run command to create deployment to create pods.
Jamies-MacBook-Pro:scripts jamie$ kubectl get pods
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
config-service-deployment-84c8fc544b-g8clz 1/1 Running 1 10h
config-service-deployment-84c8fc544b-rbjww 1/1 Running 1 10h
use ‘kubectl logs -f pod config-service-deployment-84c8fc544b-g8clz’ to check the application startup logs if you want. now, two replicas are running for config-services on port 8888, it can be accessible to other applications within K8s cluster but cannot access from outside either local host, then let’s move to the last steps.
Create service to expose service access
there are few ways to route external traffic into k8s cluster to reach pod at where the request really be handled. please refer to https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/services-networking/service/. We choose NodePort here for demonstration purpose.
config:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: config-service-service
spec:
type: NodePort
ports:
- name: http
port: 8888
targetPort: 8888
nodePort: 30001
protocol: TCP
selector:
app: config-service
nodePort: external access port, like http://localhost:30001
targetPort: port on container
port: service port, it can be used to access config-service within cluster.
create and verify the result:
Jamies-MacBook-Pro:scripts jamie$ kubectl get services
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
config-service-service NodePort 10.108.51.175 <none> 8888:30001/TCP 10h
kubernetes ClusterIP 10.96.0.1 <none> 443/TCP 174d
Jamies-MacBook-Pro:scripts jamie$ curl http://localhost:30001/catalog-service/dev/
{"name":"catalog-service","profiles":["dev"],"label":null,"version":null,"state":null,
Referred article/blogs:
https://www.jianshu.com/p/8275f2031c83
https://blog.csdn.net/kenkao/article/details/86764788
「真诚赞赏,手留余香」
真诚赞赏,手留余香
使用微信扫描二维码完成支付
