Mongo installation(for test)
docker command for local mongo installation
docker run -p 27017:27017 -v /Users/jamie/Documents/work-benches/mongo/test:/data/db --name mongo -d mongo:latest
check mongo running status
docker ps | grep mongo
9161bd4811a8 mongo:latest “docker-entrypoint.s…” 6 days ago Up 6 days 0.0.0.0:27017->27017/tcp mongo
mongo Shell installation
please refer to https://docs.mongodb.com/manual/tutorial/configure-mongo-shell/
CRUD operations
insertOne vs insertMany
insertOne - since version 3.2
insertMany - since version 3.2
MongoShell command format:

samples
to provide some samples and corresponded shell command for better understand & master each params & grammer
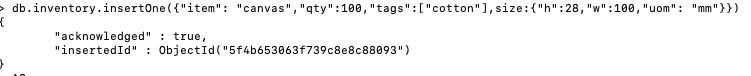
1> insert one document to inventory
db.inventory.insertOne({"item": "canvas",
"qty": 100,
"tags": ["cotton"],
size: {"h":28,"w":100,"uom": "mm"}
})
2> insert many records in same command
db.inventory.insertMany([{"item": "canvas-new",
"qty": 100,
"tags": ["cotton"],
size: {"h":28,"w":100,"uom": "mm"}
},{"item": "ipad2021",
"qty":20,
"tags":["ios","HIFI"],
size:{"h":20,"w":30,"uom": "cm"}
}])

Insert Behavior:
. Collection Creation, if the collection does not exist, the insert operation will create the collection.
. _id Field - it acts as the primary key, if an inserted document omits _id, MongoDB driver automatically generates and ObjectId for the _id fields.
. Atomicity - all wirte operation in MongoDB are automic on the level of a single document.
Find
it’s equative to SELECT in SQL, and return data in cursor.
basic grammer you should know

| SQL | MQL |
|---|---|
| a = 1 | {a: 1} |
| a <> 1 | {a: {$ne: 1}} |
| a > 1 | {a: {$gt: 1}} |
| a >= 1 | {a: {$gte: 1}} |
| a < 1 | {a: {$1t: 1}} |
| a <= 1 | {a: {$lte: 1}} |
| a = 1 and b = 1 | {a: 1, b: 1} or {$and: [{a: 1}, {b: 1}]} |
| a = 1 or b = 1 | {$or: [{a: 1}, {b: 1}]} |
| a IS NULL | {a: {$exists: false}} |
| a IN (1,2,3) | {a: {$in: [1,2,3]}} |
samples
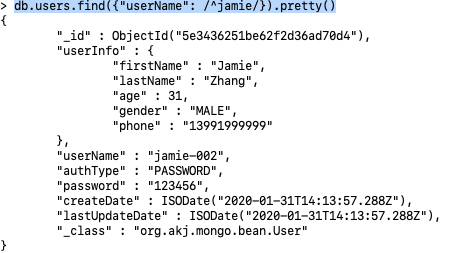
1> find users who’s userName starts with ‘jamie’
b.users.find({"userName": /^jamie/}).pretty()
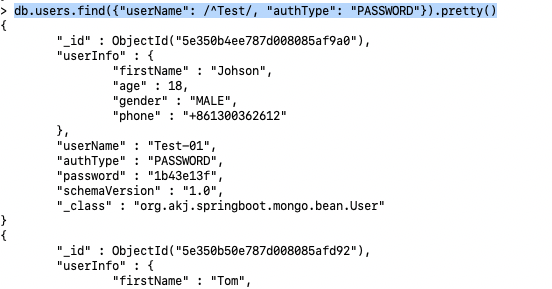
 2> find users which userName starts with 'Test' and 'authType' is 'PASSWORD'
```
db.users.find({"userName": /^Test/, "authType": "PASSWORD"}).pretty()
```
2> find users which userName starts with 'Test' and 'authType' is 'PASSWORD'
```
db.users.find({"userName": /^Test/, "authType": "PASSWORD"}).pretty()
```

3> find users who’s userName starts with ‘Test’ and ‘authType’ is ‘PASSWORD’ and his/her age between 18 and 45.
db.users.find({"userName": /^Test/, "authType": "PASSWORD","userInfo.age": {$gt: 18, $lte: 45}}).count()

4> find users which userName start with ‘Test’ and ‘authType’ is ‘PASSWORD’ and meet either of below two conditions:
– ‘userInfo.gender’ = ‘FEMALE’ and age >=3 and age < 10
– ‘userInfo.gender’ = ‘MALE’ and age >= 18 and age < 45
db.getCollection("users").find({"authType":"PASSWORD", $or: [{
"userInfo.gender": "MALE", "userInfo.age": {$gte: 18, $lt: 45}},{
"userInfo.gender": "FEMAIL", "userInfo.age": {$gte: 3, $lt: 10}
}]}).count()
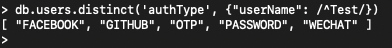
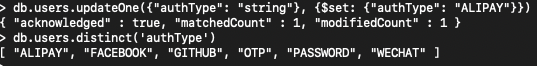
5> distinct, to find the possible values for ‘authType’
db.users.distinct('authType', {"userName": /^Test/})
 6> find users whose authType is OTP or WECHAT
```
db.getCollection("users").find({"authType": {$in : ['OTP','WECHAT']}}).limit(2).pretty()
```
6> find users whose authType is OTP or WECHAT
```
db.getCollection("users").find({"authType": {$in : ['OTP','WECHAT']}}).limit(2).pretty()
```
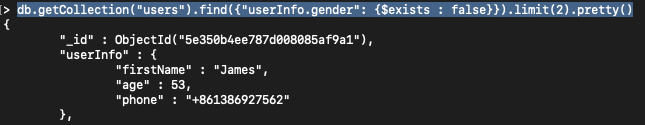
7> find users which gender is null
db.getCollection("users").find({"userInfo.gender": {$exists : false}}).limit(2).pretty()
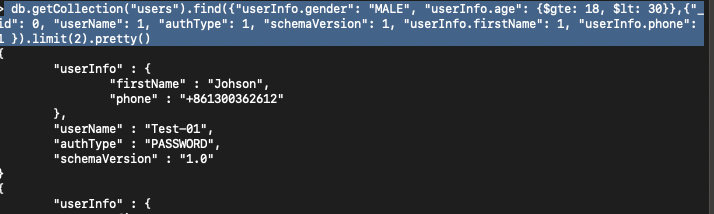
8> projection, specify the fields we need
db.getCollection("users").find({"userInfo.gender": "MALE",
"userInfo.age": {$gte: 18, $lt: 30}
},{"_id": 0,
"userName": 1,
"authType": 1,
"schemaVersion": 1,
"userInfo.firstName": 1,
"userInfo.phone": 1
}).limit(2).pretty()
Remove

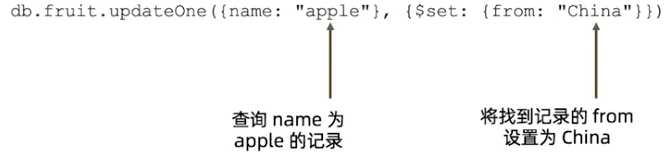
Update
basic grammers
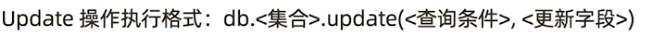


samples
1> update the authType from ‘string’ to ‘ALIPAY’
db.users.updateOne({"authType": "string"}, {$set: {"authType": "ALIPAY"}})
2> update all the documents - the ‘schemaVersion’ to ‘0.1’ if does not exist in document
db.users.updateMany({"schemaVersion": {$exists: false}}, {$set: {"schemaVersion": "0.1"}})
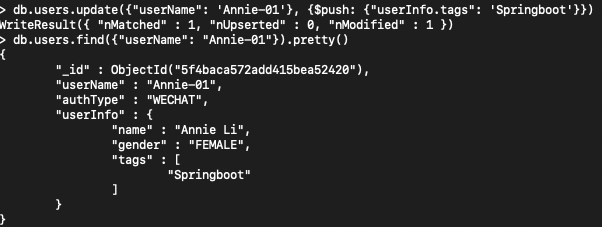
4>.add one item to an array in document
db.users.update({"userName": 'Annie-01'}, {$push: {"userInfo.tags": 'Springboot'}})
5>Add more than one items(does not exists) to an array in one go
var newTags = ['Mongodb','Angular','BlockChain']
db.users.update({"userName": 'Annie-01', 'userInfo.tags': {$ne: {$each: newTags}}}, {$addToSet: {"userInfo.tags":{$each: newTags} }})
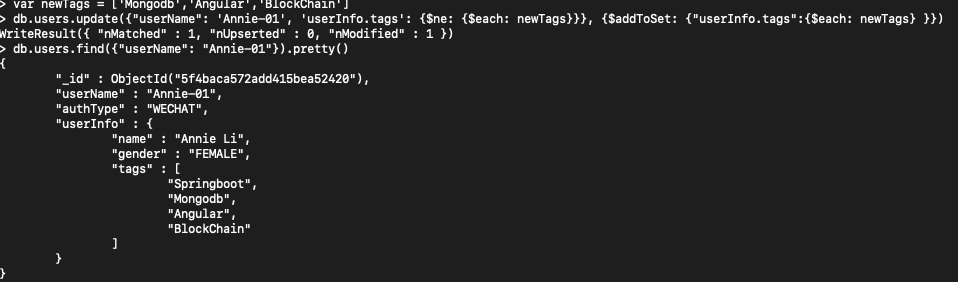 __notes:__ _this approach can also prevent duplicated data added into array_
__notes:__ _this approach can also prevent duplicated data added into array_
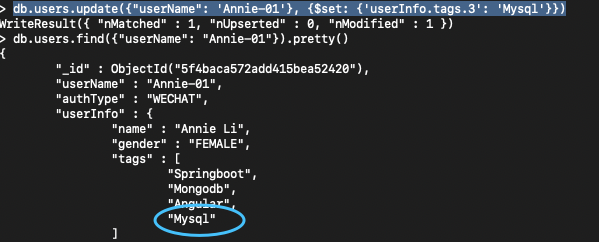
6> update the indexed data in an array
db.users.update({"userName": 'Annie-01'}, {$set: {'userInfo.tags.3': 'Mysql'}})
Drop Collection
db.
all the documents in the collection, including the indexes, will be deleted.
Drop database
db.dropDatabase()
JAVA api to do CRUD
use Document object to do CRUD
MongoDB driver
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mongodb</groupId>
<artifactId>mongo-java-driver</artifactId>
<version>${mongo.driver.version}</version>
</dependency>
insert document
@Test
public void testInsert() {
String id = UUID.randomUUID().toString();
Document userInfo = new Document().append("tags", Arrays.asList("Springboot", "Mongo"));
Document document = new Document().append("_id", id)
.append("userName", "Test-" + id.replace("-", "").substring(0, 8))
.append("authType", "WECHAT").append("createDate", new Date()).append("schemaVersion", "1.0.0").append("userInfo", userInfo);
collection.insertOne(document);
//verify the insertion
FindIterable iterable = collection.find(new BasicDBObject().append("_id", id));
Document first = (Document) iterable.first();
assertNotNull(first);
assertEquals(id, first.getString("_id"));
}
update document
@Test
public void testUpdate() {
// insert one document
String id = UUID.randomUUID().toString();
Document userInfo = new Document().append("tags", Arrays.asList("Springboot", "Mongo"));
Document document = new Document().append("_id", id)
.append("userName", "Test-" + id.replace("-", "").substring(0, 8))
.append("authType", "WECHAT").append("createDate", new Date()).append("schemaVersion", "1.0.0").append("userInfo", userInfo);
collection.insertOne(document);
// try to update it
//Document update = new Document().append("tags", Arrays.asList("Mysql","Scala"));
collection.updateOne(document, new Document("$addToSet", new Document("userInfo.tags", new Document("$each", Arrays.asList("Mysql", "Scala")))));
// find the document and check the update
FindIterable iterable = collection.find(new BasicDBObject().append("_id", id));
Document first = (Document) iterable.first();
assertNotNull(first);
assertEquals(4, ((List<String>) (((Document) first.get("userInfo")).get("tags"))).size());
}
use gson + POJO to do CRUD
1> define customize codec if need to do the date type that does not support by MongoDB by default
public class DateCodec implements Codec<Date> {
@Override
public Date decode(BsonReader reader, DecoderContext decoderContext) {
Date date = null;
try {
reader.readStartDocument();
date = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-mm-dd hh:MM:ss").parse(reader.readString("dateTime"));
reader.readEndDocument();
} catch (ParseException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return date;
}
@Override
public void encode(BsonWriter writer, Date value, EncoderContext encoderContext) {
writer.writeStartDocument();
writer.writeString("dateTime", new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-mm-dd hh:MM:ss").format(value));
writer.writeEndDocument();
}
@Override
public Class<Date> getEncoderClass() {
return Date.class;
}
}
2> POJO
@Data
public class User implements Serializable {
@BsonId
@BsonProperty("_id")
private String id;
private UserInfo userInfo;
private String userName;
private String authType;
private String password;
@BsonProperty("createDate")
private Date createDate;
private Date lastUpdateDate;
}
@Data
public class UserInfo implements Serializable {
private String firstName;
private String middleName;
private String lastName;
private int age;
private GenderEnum gender;
private String phone;
private String telPhone;
}
public enum GenderEnum {
MALE,FEMALE,OTHER;
}
3> test cases
public class MongoClientTest {
private MongoClient client;
private static final String url = "mongodb://localhost:27017";
private static final String DATABASE = "test";
private static final String COLLECTION = "users";
private MongoCollection collection;
@BeforeEach
public void setup() {
MongoClientURI clientURI = new MongoClientURI(url);
client = new MongoClient(clientURI);
PojoCodecProvider pojoCodecProvider =
PojoCodecProvider.builder().register("org.akj.mongo.bean").conventions(Arrays.asList(Conventions.ANNOTATION_CONVENTION, Conventions.OBJECT_ID_GENERATORS, Conventions.CLASS_AND_PROPERTY_CONVENTION)).build();
CodecRegistry pojoCodecRegistry = fromRegistries(MongoClient.getDefaultCodecRegistry(),
fromProviders(pojoCodecProvider));
MongoDatabase database = client.getDatabase(MongoClientTest.DATABASE);
boolean collectionExists = client.getDatabase(DATABASE).listCollectionNames()
.into(new ArrayList<String>()).contains(COLLECTION);
if (!collectionExists) {
database.createCollection("users");
collection =
database.getCollection("users", User.class).withCodecRegistry(pojoCodecRegistry);
IndexOptions indexOptions = new IndexOptions();
indexOptions.unique(true);
indexOptions.name("users_uni_username");
collection.createIndex(new Document("userName", 1), indexOptions);
}
collection =
database.getCollection(MongoClientTest.COLLECTION).withCodecRegistry(pojoCodecRegistry);
}
@Test
public void testConnection() {
Assertions.assertNotNull(client, "mongo db connection issue");
MongoIterable<String> actual = client.listDatabaseNames();
Assertions.assertNotNull(actual);
log.info("{}", actual);
actual.forEach((Consumer<? super String>) s -> log.info(s));
}
@Test
public void testInsert() {
UserInfo userInfo = new UserInfo();
userInfo.setFirstName("Jamie");
userInfo.setLastName("Zhang");
userInfo.setAge(31);
userInfo.setGender(GenderEnum.MALE);
userInfo.setPhone("13991999999");
User u = new User();
u.setUserInfo(userInfo);
u.setAuthType("PASSWORD");
u.setUserName("jamie-002");
u.setPassword("123456");
Date date = new Date();
u.setCreateDate(date);
u.setLastUpdateDate(date);
Gson gson = new Gson();
Document document = Document.parse(gson.toJson(u));
collection.insertOne(document);
}
@Test
public void testDuplicateKey() {
Assertions.assertThrows(MongoWriteException.class, () -> {
testInsert();
testInsert();
});
}
@Test
public void testFindOne() {
Gson gson = new Gson();
FindIterable iterable = collection.find();
MongoCursor cursor = iterable.cursor();
while (cursor.hasNext()) {
Object obj = cursor.next();
Document doc = (Document) obj;
String json = doc.toJson(JsonWriterSettings.builder().build());
User u = gson.fromJson(json, User.class);
log.debug("{}", u);
}
}
@Test
public void testDropCollection() {
MongoDatabase database = client.getDatabase(MongoClientTest.DATABASE);
MongoCollection<Document> collection = database.getCollection(MongoClientTest.COLLECTION);
if (null != collection) collection.drop();
Assertions.assertNull(database.getCollection(MongoClientTest.COLLECTION));
}
}
「真诚赞赏,手留余香」
真诚赞赏,手留余香
使用微信扫描二维码完成支付
